
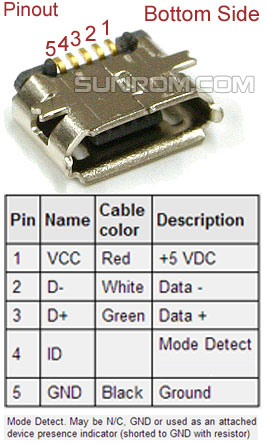
These remote devices use this upstream connection to connect to a host. So, to establish a connection, USB remote devices feature what we call an upstream connection. It’s essential to make correct USB connections to allow the system to follow the required USB protocol. Like all connectors, all types of USB connectors have male and female types, making sure you connect your devices in the right direction. Check out the table below for the full USB pinout. Two of these wires are for power supply, while the other two are for differential data signal pairs. The USB has four shielded wires that work as pins. So, in this article, we’ll explain everything about the USB and give different USB examples for your circuits. However, that’s just the surface of it all. Also, there are cases where you can add additional USB network hubs to create a tree connection structure. Normally, the architecture of a USB system includes a host controller, USB ports, and a wide variety of devices. USB stands for Universal Serial Bus and has since replaced its predecessors (FireWire, RS-232 serial, and even parallel) as the primary interface for connecting a host to a device. In the compatibility mode (USB 1.0 or USB 2.0) communication is half-duplex, with direction controlled by the host.Nowadays, it’s easy to complete projects that involve creating a physical connection between a host controller and several other bus-powered devices because of the USB interface. USB 3.1 is the successor standard (USB 3.1 Gen 2), was released in July 2013 with the new transfer mode SuperSpeed+ that can transfer data at up to 10 Gbit/s (1.25 GB/s, twice the rate of USB 3.0).Ĭommunication is full-duplex during SuperSpeed. USB 3.0 connectors are usually distinguished from their USB 2.0 counterparts by blue color-coding of the receptacles and plugs. USB 3.0 combines USB 2.0 bus and new SuperSpeed bus with transfer rate up to 5.0 Gbit/s, which is about ten times faster than the USB 2.0 standard.
USB 3.0 is the third major version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard for interfacing computers and electronic devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
